Common stainless steel knowledge
Steel is a general term for iron-carbon alloys with carbon content between 0.02% and 2.11%. More than 2.11% is iron.
The chemical composition of steel can vary greatly. Steel containing only carbon is called carbon steel or ordinary steel. In the smelting process of steel, chromium, nickel, manganese, silicon, titanium, molybdenum and other alloy elements can also be added to improve the properties of steel.
Stainless steel is a steel with the main characteristics of rust resistance and corrosion resistance, and the chromium content is at least 10.5%, and the carbon content is not more than 1.2%.
1. Stainless steel will not rust?
When there are brown rust spots (spots) on the surface of stainless steel, people are surprised. They think that stainless steel will not rust. Rust is not stainless steel. It may be due to the problem of steel quality. In fact, this is a one-sided wrong view of the lack of understanding of stainless steel. Stainless steel will rust under certain conditions. Stainless steel has the ability to resist atmospheric oxidation – rust resistance, and also has the ability to resist corrosion in the medium containing acid, alkali and salt, that is, corrosion resistance. However, its corrosion resistance varies with its chemical composition, mutual state, service conditions and environmental media type. For example, 304 material has absolutely excellent corrosion resistance in dry and clean atmosphere, but when it is moved to the coastal area, it will soon rust in the sea fog containing a lot of salt. Therefore, not any kind of stainless steel can resist corrosion and rust at any time. Stainless steel is a very thin, solid and fine stable chromium-rich oxide film (protective film) formed on its surface to prevent oxygen atoms from continuing to penetrate and oxidize, thus obtaining the ability to resist corrosion. Once for some reason, the film is constantly damaged, the oxygen atoms in the air or liquid will continue to penetrate or the iron atoms in the metal will continue to separate, forming loose iron oxide, and the metal surface will also be constantly corroded.
2. What kind of stainless steel is not easy to rust?
There are three main factors affecting stainless steel corrosion.
1) Content of alloying elements
Generally speaking, steel with 10.5% chromium content is not easy to rust. The higher the content of chromium and nickel, the better the corrosion resistance. For example, the content of 304 material nickel is 8%~10%, and the content of chromium is 18%~20%. Such stainless steel will not rust under normal circumstances.
2) Smelting process of production enterprises
The smelting process of the production enterprise will also affect the corrosion resistance of stainless steel. Large stainless steel plants with good smelting technology, advanced equipment and advanced technology can be guaranteed in terms of the control of alloying elements, the removal of impurities, and the control of billet cooling temperature. Therefore, the product quality is stable and reliable, the internal quality is good, and it is not easy to rust. On the contrary, some small steel plants are backward in equipment and technology. During the smelting process, impurities cannot be removed, and the products produced will inevitably rust.
3) External environment
The environment with dry climate and good ventilation is not easy to rust. However, areas with high air humidity, continuous rainy weather, or high acidity and alkalinity in the air are prone to rust. 304 stainless steel will rust if the surrounding environment is too poor.
3. How to deal with rusty spots on stainless steel?
1) Chemical methods
Use acid cleaning paste or spray to assist the rusted parts to passivate again to form chromium oxide film to restore their corrosion resistance. After acid cleaning, in order to remove all pollutants and acid residues, it is very important to properly rinse with clean water. After all treatment, re-polish with polishing equipment and seal with polishing wax. For parts with slight rust spots, 1:1 gasoline and engine oil mixture can also be used to wipe the rust spots with clean rags.
2) Mechanical method
Blast cleaning, shot blasting with glass or ceramic particles, annihilation, brushing and polishing. It is possible to wipe away the pollution caused by previously removed materials, polishing materials or annihilated materials by mechanical methods. All kinds of pollution, especially foreign iron particles, may become the source of corrosion, especially in humid environment. Therefore, the mechanically cleaned surface should be formally cleaned under dry conditions. The use of mechanical method can only clean its surface and cannot change the corrosion resistance of the material itself. Therefore, it is recommended to re-polish with polishing equipment after mechanical cleaning, and seal with polishing wax.
4. Can stainless steel be judged by magnet?
Many people go to buy stainless steel or stainless steel products and bring a small magnet with them. When they look at the goods, they think that good stainless steel is the one that can’t be absorbed. Without magnetism, there will be no rust. In fact, this is a wrong understanding.
The non-magnetic stainless steel band is determined by the structure. During the solidification process of molten steel, due to the different solidification temperature, it will form stainless steel with different structure such as “ferrite”, “austenite” and “martensite”, among which “ferrite” and “martensite” stainless steel are magnetic. The “austenitic” stainless steel has good comprehensive mechanical properties and weldability, but the “ferritic” stainless steel with magnetism is stronger than the “austenitic” stainless steel only in terms of corrosion resistance.
At present, the so-called 200 series and 300 series stainless steels with high manganese content and low nickel content in the market also do not have magnetism, but their performance is far from that of 304 with high nickel content. On the contrary, 304 will also have micro-magnetism after stretching, annealing, polishing, casting and other processes. Therefore, it is a misunderstanding and unscientific to judge the advantages and disadvantages of stainless steel by using stainless steel without magnetism.
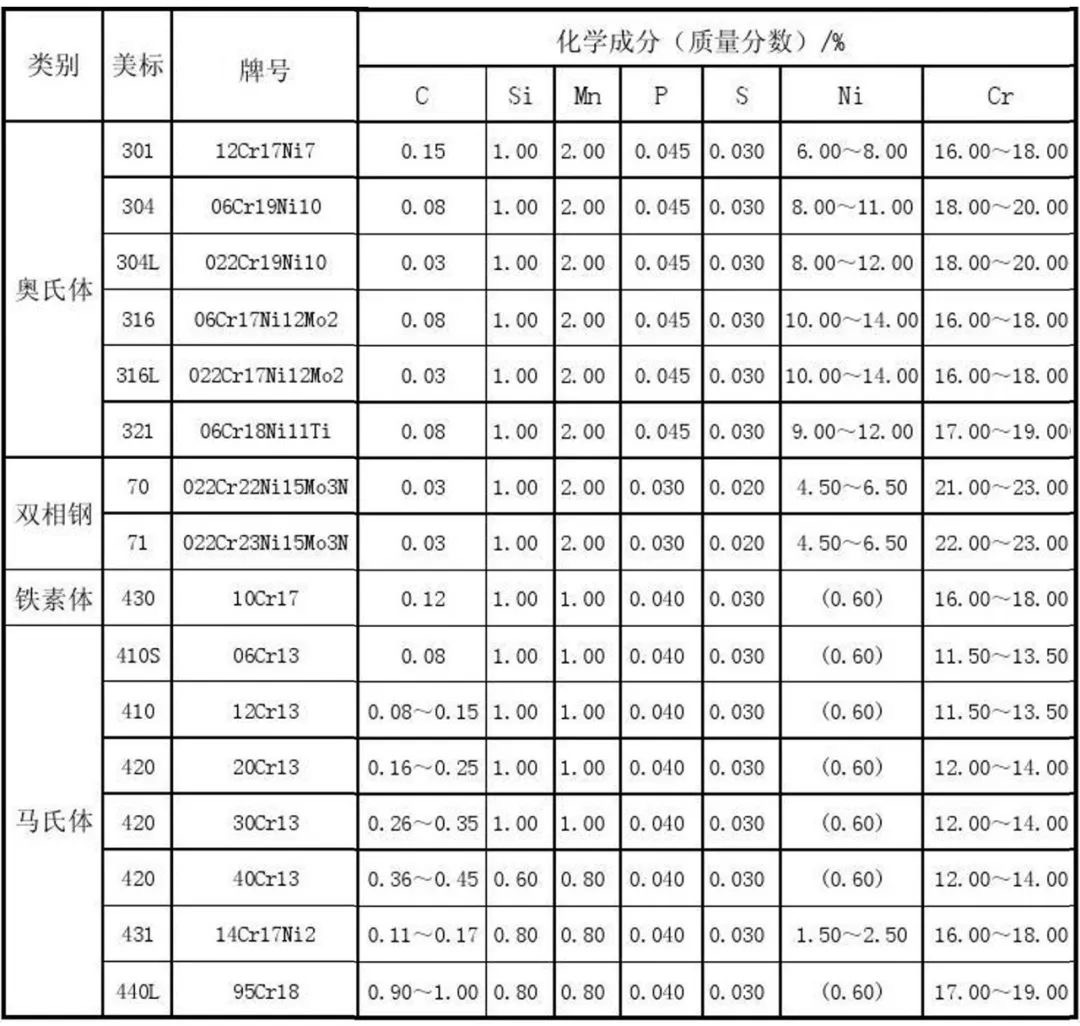
5. What are the brands of commonly used stainless steel?
201: Manganese is used instead of nickel stainless steel, which has certain acid and alkali resistance, high density, polishing and no bubbles. It is applied to watch cases, decorative tubes, industrial tubes and other shallow drawn products.
202: It belongs to low nickel and high manganese stainless steel, with nickel and manganese content of about 8%. Under weak corrosion conditions, it can replace 304, with high cost performance. It is mainly used in building decoration, highway guardrail, municipal engineering, glass handrail, highway facilities, etc.
304: General stainless steel, with good corrosion resistance, heat resistance, low temperature strength and mechanical properties, and high toughness, is used in food industry, medical industry, industry, chemical industry, and home decoration industry.
304L: low carbon 304 stainless steel, used for equipment parts with corrosion resistance and formability.
316: With the addition of Mo, it has excellent high temperature corrosion resistance and is applied in the fields of seawater equipment, chemistry, food industry and paper making.
321: It has excellent high temperature stress breaking performance and high temperature creep resistance.
430: Heat resistant fatigue, thermal expansion coefficient is smaller than that of austenite, and it is applied to household appliances and architectural decoration.
410: It has high hardness, toughness, good corrosion resistance, large thermal conductivity, small expansion coefficient, and good oxidation resistance. It is used to manufacture atmospheric, water vapor, water and oxidizing acid corrosive parts.
The following is the content table of “alloy elements” of different steel grades of common stainless steel for reference only:
Post time: Jan-30-2023